ICD-10 Degeneration Of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Managing The Condition
Alright, let’s dive into something that affects millions worldwide but often gets overlooked until it becomes a major issue. ICD-10 degeneration of lumbar intervertebral disc is one of those medical terms that sounds super complicated, but it’s actually quite straightforward once you break it down. This condition refers to the gradual wear and tear of the discs in your lower back, which can lead to discomfort, pain, and even mobility issues if left untreated. If you’ve been diagnosed with this or suspect you might have it, you’re in the right place. In this guide, we’ll break it all down for you—what it is, how it happens, and most importantly, what you can do about it.
Now, let’s be real here. Back pain isn’t something you want to mess around with. It can creep up on you without warning, making simple tasks like bending over or sitting for long periods feel like torture. And when it comes to the lumbar region, which supports most of your body weight, the stakes are even higher. The good news? Understanding the ICD-10 classification for degenerative disc disease (DDD) can help you get the right diagnosis and treatment plan. So, buckle up because we’re about to cover everything you need to know!
Before we jump into the nitty-gritty, let’s set the stage. This guide isn’t just about throwing medical jargon at you. We’re here to make sure you leave with actionable insights and a clear understanding of how to manage and prevent further damage. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, this article has got your back—pun intended. Let’s get started!
- What Is Alanon Meaning Unlock The Secrets To Support And Recovery
- Sign Matches For Taurus Unlocking The Secrets Of Cosmic Compatibility
Understanding ICD-10 Degeneration of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc
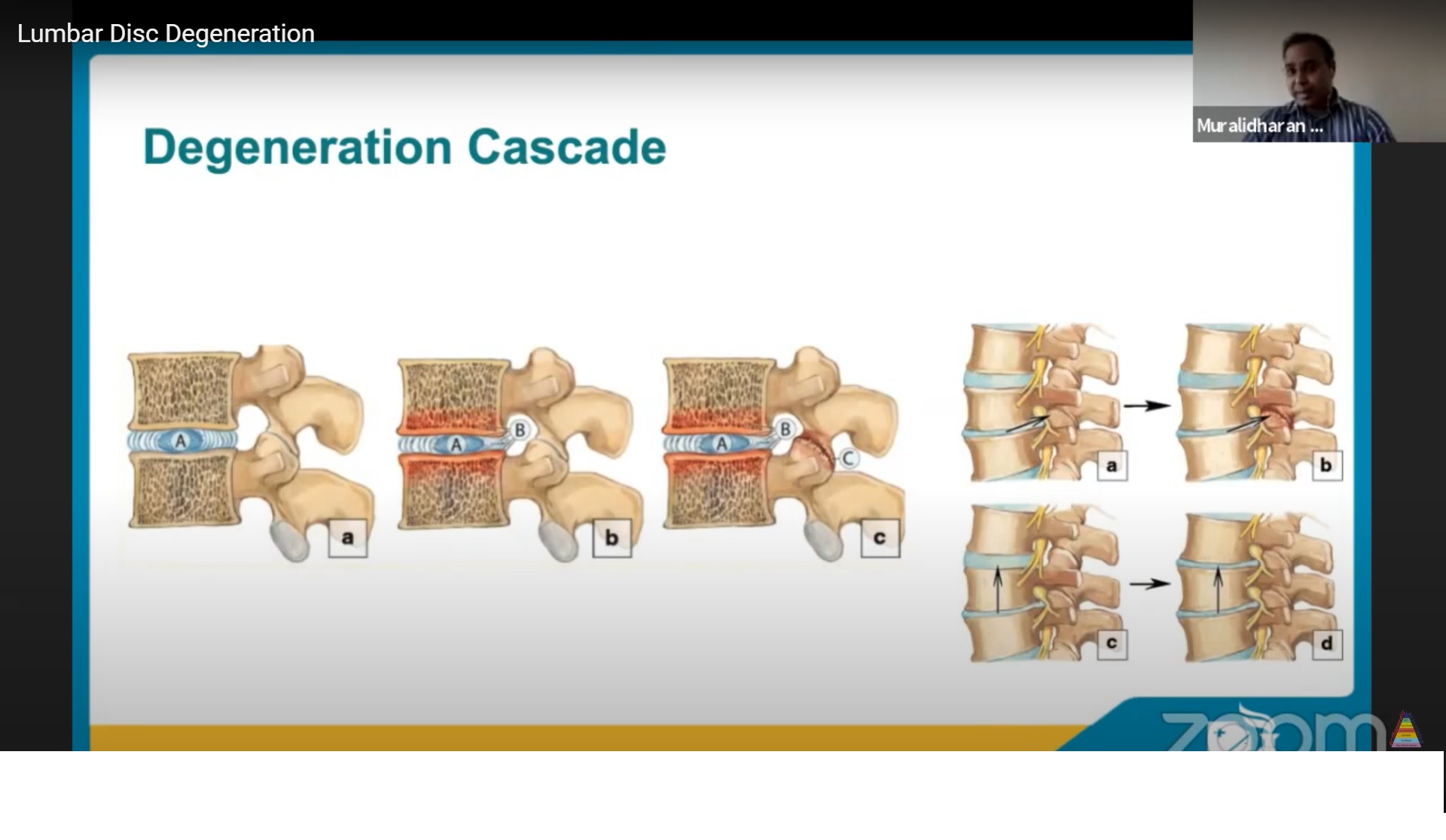
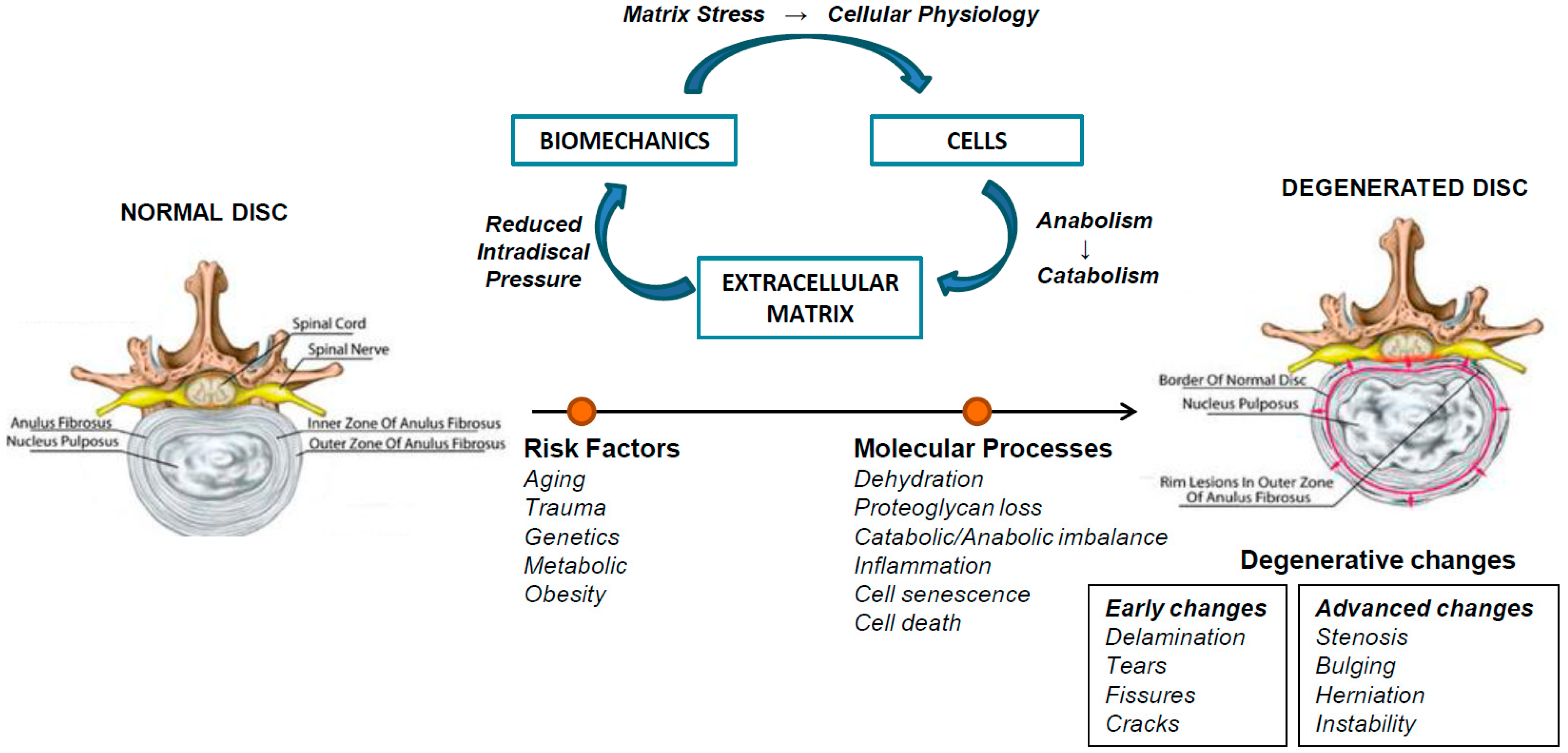
First things first, let’s talk about what exactly we mean by "ICD-10 degeneration of lumbar intervertebral disc." The ICD-10 code M51.2 is specifically assigned to this condition, which refers to the degeneration of discs located in the lumbar region of your spine. These discs act as cushions between the vertebrae, allowing for smooth movement and shock absorption. Over time, due to age, injury, or other factors, these discs can deteriorate, leading to pain and reduced functionality.
Here’s a quick breakdown of what happens:
- The discs lose water content, making them less flexible.
- Cracks or tears may develop in the outer layer of the disc.
- In some cases, the inner gel-like material can leak out, causing irritation to nearby nerves.
And let’s not forget the symptoms. People with lumbar disc degeneration often experience lower back pain, stiffness, and sometimes even radiating pain down the legs. It’s not fun, but the earlier you catch it, the better your chances of managing it effectively.
- Mastering The Conversion Of Fahrenheit To Celsius A Comprehensive Guide For Everyday Use
- Alfalfa The Character The Beloved Icon In Popular Culture
What Causes Lumbar Disc Degeneration?
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s dig deeper into the causes. While aging is a primary factor, there are other contributors to consider:
- Injury: Trauma to the back, such as from a fall or car accident, can accelerate disc degeneration.
- Repetitive Stress: Jobs or activities that involve heavy lifting or prolonged sitting can put extra strain on the lumbar discs.
- Genetics: Some people are simply more predisposed to developing disc problems due to their genetic makeup.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, obesity, and lack of exercise can all increase the risk of disc degeneration.
It’s important to note that while some factors are out of your control, others can be managed with lifestyle changes. We’ll touch on that later in the article.
ICD-10 Codes: Why They Matter
ICD-10 codes are essentially the language of healthcare. They’re used by doctors, insurance companies, and researchers to classify and track medical conditions. For lumbar disc degeneration, the code M51.2 is your go-to reference. But why does this matter to you? Well, having the correct code ensures that you receive the appropriate treatment and that your insurance covers it. It also helps healthcare providers communicate more effectively about your condition.
Let’s say you’re seeing a new doctor. Instead of explaining your entire medical history, you can simply provide the ICD-10 code, and they’ll know exactly what you’re dealing with. Pretty convenient, right? Plus, these codes play a crucial role in global health research, helping experts track trends and develop better treatments.
How ICD-10 Codes Are Used in Diagnosis
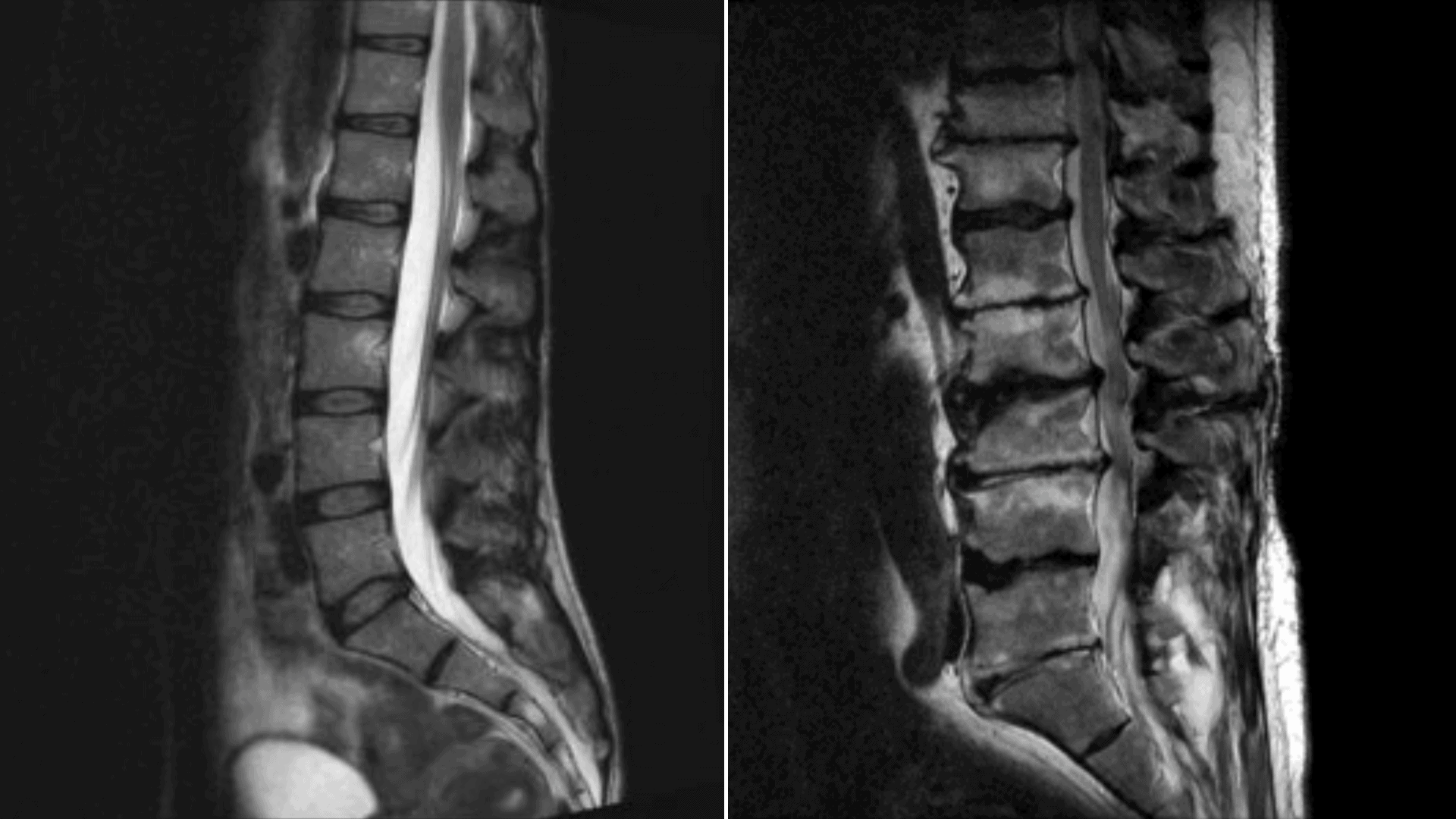
When you visit a healthcare professional, they’ll likely perform a physical exam and review your medical history. If they suspect lumbar disc degeneration, they may order imaging tests like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to confirm the diagnosis. Once they’ve gathered all the necessary information, they’ll assign the appropriate ICD-10 code to your condition.
This code isn’t just for labeling purposes—it’s a vital tool in guiding treatment decisions. For example, if your code indicates mild degeneration, your doctor might recommend conservative treatments like physical therapy and medication. On the other hand, if the code reflects severe degeneration, surgery might be considered as an option.
Symptoms of Lumbar Disc Degeneration
Alright, let’s talk about the elephant in the room: symptoms. While everyone’s experience may vary, there are some common signs to look out for:
- Persistent Lower Back Pain: This is often the first red flag. The pain can range from mild to severe and may worsen with certain activities.
- Stiffness: You might notice that your lower back feels stiff, especially in the morning or after long periods of inactivity.
- Radiating Pain: Some people experience pain that radiates down the legs, a condition known as sciatica.
- Weakness or Numbness: In more advanced cases, you might feel weakness or numbness in the legs or feet.
It’s important to pay attention to these symptoms and seek medical advice if they persist or worsen. Early intervention can make a big difference in managing the condition.
Diagnosing Lumbar Disc Degeneration
So, how do doctors determine if you have lumbar disc degeneration? It starts with a thorough evaluation, which may include:
- A physical exam to assess your range of motion and identify tender areas.
- A review of your medical history to look for patterns or risk factors.
- Imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans, to visualize the discs and surrounding structures.
Once all the information is gathered, your doctor will use the ICD-10 code to classify the severity of your condition and develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Treatment Options for Lumbar Disc Degeneration
Now that we’ve covered the diagnosis, let’s talk about what you can do about it. The good news is that there are several treatment options available, ranging from conservative therapies to more invasive procedures. The key is finding the right approach for your specific situation.
Here are some common treatments:
- Physical Therapy: This can help strengthen the muscles supporting your spine and improve flexibility.
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation around the affected area.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged discs or fuse vertebrae together.
It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action. What works for one person may not work for another, so personalized care is key.
Preventing Further Degeneration
While you can’t completely stop the aging process, there are steps you can take to slow down disc degeneration and prevent further damage:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts extra strain on your spine, so staying within a healthy weight range is crucial.
- Exercise Regularly: Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or yoga can help keep your spine strong and flexible.
- Practice Good Posture: Whether you’re sitting, standing, or lifting, proper posture can reduce stress on your discs.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can accelerate disc degeneration, so quitting is one of the best things you can do for your spine.
By making these lifestyle changes, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing or worsening lumbar disc degeneration.
Living with Lumbar Disc Degeneration
Let’s be honest—living with a chronic condition like lumbar disc degeneration isn’t always easy. But with the right mindset and strategies, you can still lead a fulfilling life. The key is finding ways to adapt and manage your symptoms effectively.
Here are some tips for living with lumbar disc degeneration:
- Stay Active: Regular exercise can help improve your overall well-being and reduce pain.
- Use Assistive Devices: Tools like ergonomic chairs or lumbar support pillows can make a big difference in your daily life.
- Seek Support: Joining a support group or talking to others with similar experiences can provide emotional relief and practical advice.
- Stay Positive: Maintaining a positive outlook can help you cope with the challenges of living with a chronic condition.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Millions of people around the world are managing lumbar disc degeneration successfully, and you can too.
Coping with Pain and Limitations
Pain management is often a major concern for those with lumbar disc degeneration. While medication can provide temporary relief, there are other techniques you can try:
- Heat or Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to relieve pain.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Techniques like deep breathing and meditation can help you manage stress and reduce pain perception.
Experiment with different methods to see what works best for you. Everyone’s experience is unique, so it may take some trial and error to find the right combination of treatments.
Conclusion
Alright, we’ve covered a lot of ground here, and hopefully, you now have a better understanding of ICD-10 degeneration of lumbar intervertebral disc. From the basics of what it is to the various treatment options available, this condition doesn’t have to control your life. By staying informed and proactive, you can manage your symptoms and maintain a high quality of life.
So, what’s next? If you suspect you have lumbar disc degeneration, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Early diagnosis and treatment can make a world of difference. And if you’re already managing the condition, remember to prioritize self-care and explore all the available resources to support your journey.
Feel free to leave a comment below with any questions or insights. Share this article with someone who might find it helpful, and don’t forget to explore our other content for more tips on maintaining a healthy spine. Your back will thank you!
Table of Contents
- Understanding ICD-10 Degeneration of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc
- What Causes Lumbar Disc Degeneration?
- ICD-10 Codes: Why They Matter
- Symptoms of Lumbar Disc Degeneration
- Diagnosing Lumbar Disc Degeneration
- Treatment Options for Lumbar Disc Degeneration
- Preventing Further Degeneration
- Living with Lumbar Disc Degeneration
- Coping with Pain and Limitations
- Conclusion
- Soaring High The Thrilling World Of French Pole Vault
- James Mitchum Movies A Deep Dive Into The Legacy Of A Hollywood Icon
Lumbar Disc Degeneration and Herniation —
Disc Degeneration Backspace
Degenerative Disc Disease Lumbar Icd 10 Quotes Trendy