Exploring The Everglades Ecosystem Food Web: A Naturalist’s Paradise
When you think about the Everglades, what comes to mind? A sprawling wetland teeming with life, where every creature plays a crucial role in the grand scheme of nature. The Everglades ecosystem food web is a fascinating web of interactions that sustain life in one of the most unique environments on Earth. It’s not just a habitat; it’s a living, breathing testament to the delicate balance of nature. If you’re diving into this topic, you’re about to uncover the secrets of how life thrives in the swampy wonderland of Florida.
Picture this: an intricate dance of predators and prey, plants and animals, all intertwined in a complex network that’s been fine-tuned over millennia. The Everglades is more than just a tourist attraction—it’s a living laboratory where every species, from the tiniest insect to the majestic alligator, has a part to play. Understanding the food web here isn’t just about knowing what eats what; it’s about appreciating the interconnectedness of life.
As we journey through this article, you’ll discover how the Everglades food web works, the key players involved, and why it’s so important to preserve this ecosystem. Whether you’re a nature enthusiast, a student, or just someone curious about the world around you, this deep dive into the Everglades’ natural order is sure to fascinate. Let’s get started!
- Projocom Obituary A Comprehensive Guide To Honoring Lives
- 73 Fahrenheit To Celsius The Ultimate Guide To Temperature Conversion
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Everglades Ecosystem
- Understanding the Food Web Concept
- Key Players in the Everglades Food Web
- Producers: The Foundation of Life
- Primary Consumers: The Herbivores
- Secondary Consumers: The Carnivores
- Decomposers: Nature’s Clean-Up Crew
- Interactions in the Food Web
- Threats to the Everglades Food Web
- Conservation Efforts
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Introduction to the Everglades Ecosystem
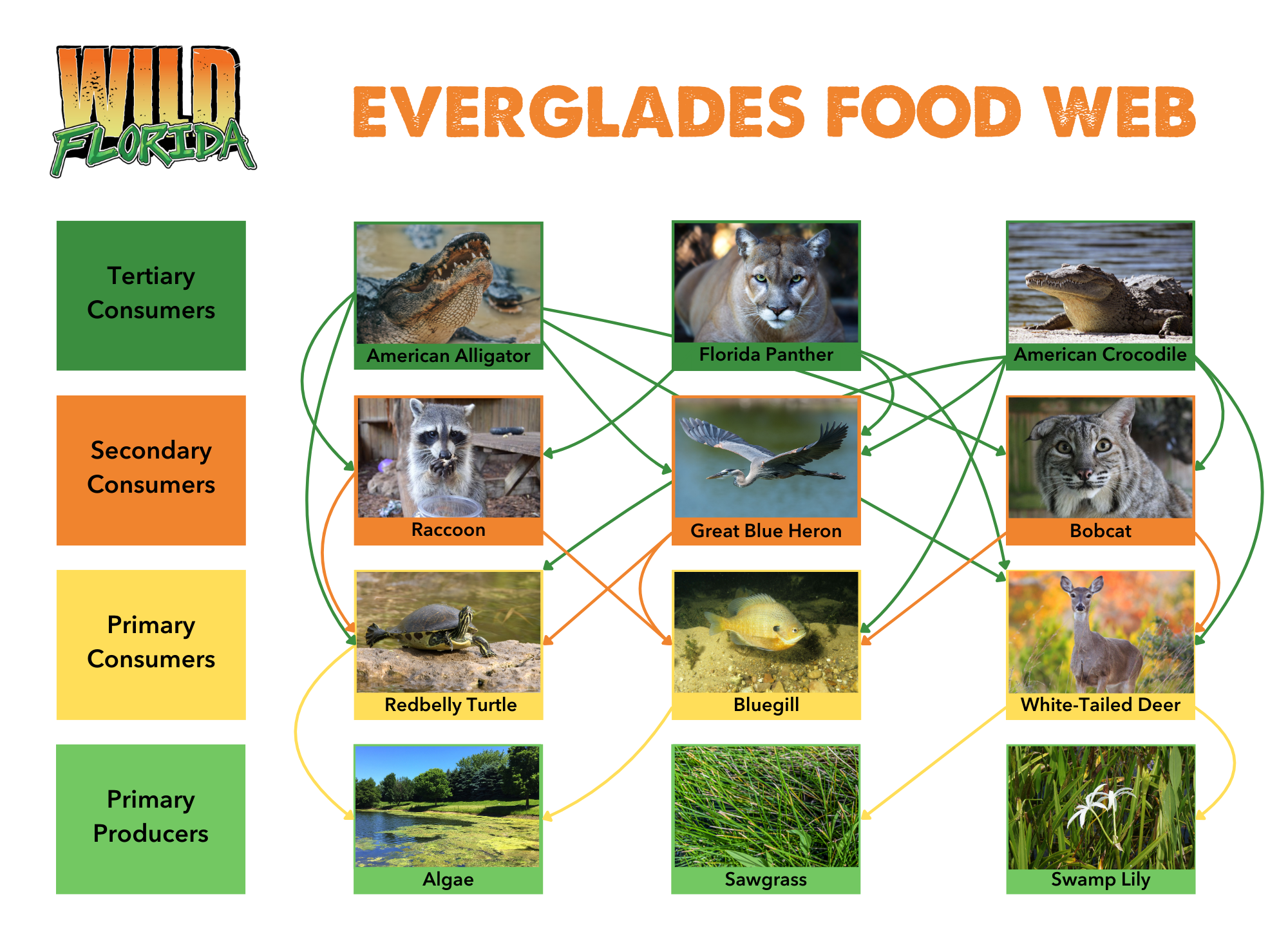
The Everglades ecosystem is often described as a "river of grass," but it’s so much more than that. It’s a vast wetland that stretches across southern Florida, home to countless species of plants and animals. The food web here is what keeps the entire system in balance. Without it, the Everglades as we know it would cease to exist.
This ecosystem is unique because of its mix of freshwater and saltwater habitats. It’s a place where mangroves meet marshes, and where alligators swim alongside manatees. The food web in the Everglades is a complex network that supports everything from microscopic plankton to the apex predators at the top of the chain.
- When Is Frankie Beverly Funeral Date A Tribute To A Musical Legend
- Soaring High The Thrilling World Of French Pole Vault
Understanding the Food Web Concept
A food web is like a map of who eats whom in an ecosystem. It’s not a simple chain but a web of relationships. In the Everglades, the food web starts with producers—plants that create their own food through photosynthesis. These producers are eaten by primary consumers, or herbivores, which are then preyed upon by secondary consumers, or carnivores. And the cycle continues.
What Makes the Everglades Food Web Unique?
Unlike many other ecosystems, the Everglades food web is heavily influenced by seasonal changes. During the dry season, water levels drop, concentrating prey in smaller areas. This makes hunting easier for predators like alligators and herons. In the wet season, the food web expands as water covers more ground, allowing species to spread out.
Key Players in the Everglades Food Web
Every species in the Everglades plays a vital role in the food web. Here’s a look at some of the main players:
- Alligators: Apex predators that keep populations of smaller animals in check.
- Manatees: Gentle giants that graze on seagrass and other aquatic plants.
- Herons: Wading birds that feed on fish and small aquatic animals.
- Snails: Tiny creatures that are an important food source for many animals.
How Do These Species Interact?
Each species has its own niche in the food web. For example, alligators prey on fish, birds, and even small mammals. Manatees, on the other hand, are herbivores that help control the growth of aquatic plants. Snails might seem insignificant, but they’re a crucial food source for many wading birds.
Producers: The Foundation of Life
At the base of the Everglades food web are the producers. These are plants like sawgrass, mangroves, and algae that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Without them, there would be no food for the rest of the ecosystem.
Why Are Producers So Important?
Producers are the foundation of the food web because they provide energy for all other organisms. They also help purify the water and provide habitat for countless species. In the Everglades, sawgrass is especially important because it creates dense stands that protect smaller animals from predators.
Primary Consumers: The Herbivores
Primary consumers are the next level up in the food web. These are animals like manatees, turtles, and insects that feed directly on plants. They play a crucial role in controlling plant populations and providing food for predators.
Examples of Primary Consumers
- Manatees graze on seagrass and other aquatic plants.
- Turtles eat algae and other vegetation.
- Insects feed on leaves and flowers.
Secondary Consumers: The Carnivores
Secondary consumers are the predators in the Everglades food web. These include animals like alligators, herons, and otters. They feed on primary consumers and help keep their populations in check.
What Do Secondary Consumers Eat?
Secondary consumers have a varied diet depending on their species. For example:
- Alligators eat fish, birds, and small mammals.
- Herons feed on fish, frogs, and insects.
- Otters hunt for fish and crayfish.
Decomposers: Nature’s Clean-Up Crew
Decomposers are often overlooked, but they’re just as important as producers and consumers. These are organisms like fungi, bacteria, and insects that break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Why Are Decomposers Essential?
Decomposers are the recyclers of the Everglades. They break down dead plants and animals, releasing nutrients back into the soil and water. This process is vital for maintaining the health of the ecosystem.
Interactions in the Food Web
The Everglades food web is full of interactions that keep the ecosystem in balance. Predation, competition, and symbiosis are just a few examples of these interactions.
Predation
Predation is when one animal hunts and eats another. In the Everglades, alligators are some of the most effective predators. They help control populations of fish, birds, and mammals, preventing any one species from becoming too dominant.
Competition
Competition occurs when two or more species vie for the same resources. For example, different species of fish might compete for the same food sources. This competition helps drive evolution and adaptation in the ecosystem.
Symbiosis
Symbiosis is a relationship between two species where both benefit. In the Everglades, symbiosis can be seen in the relationship between mangroves and oysters. Mangroves provide a habitat for oysters, while oysters help filter the water, benefiting the mangroves.
Threats to the Everglades Food Web
Despite its resilience, the Everglades food web faces numerous threats. Pollution, habitat loss, and invasive species are just a few of the challenges this ecosystem must overcome.
Invasive Species
Invasive species like the Burmese python can wreak havoc on the food web. These snakes have no natural predators in the Everglades and prey on native species, disrupting the balance of the ecosystem.
Pollution
Pollution from agricultural runoff and urban development can harm the water quality in the Everglades. This affects not only the plants and animals but also the people who rely on this ecosystem for clean water.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are crucial for protecting the Everglades food web. Organizations and governments are working together to restore habitats, control invasive species, and reduce pollution.
Restoration Projects
Restoration projects aim to return the Everglades to its natural state. This includes restoring water flow, replanting native vegetation, and removing invasive species.
Public Awareness
Raising public awareness is also important. Educating people about the importance of the Everglades and how they can help protect it is key to long-term conservation success.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
The Everglades ecosystem food web is a marvel of nature. It’s a complex network of interactions that sustain life in one of the most unique environments on Earth. By understanding how this food web works, we can appreciate the importance of preserving this ecosystem for future generations.
So, what can you do to help? Start by learning more about the Everglades and sharing your knowledge with others. Support conservation efforts and reduce your own impact on the environment. Together, we can ensure that the Everglades food web remains vibrant and healthy for years to come.
Feel free to leave a comment or share this article with your friends. Let’s keep the conversation going and work together to protect this natural treasure!
- Is Neosporin Safe For Lips The Ultimate Guide To Healing And Protecting Your Pout
- Broward County Sheriff Inmate Search Your Ultimate Guide To Finding Inmate Records

Everglades Ecosystem Audubon
The Everglades Food Web A Unique Ecosystem

Everglades Ecosystem stock photo. Image of branch, everglades 6163830