Unveiling The Earth's Diameter In Miles: A Journey Through Our Planet's Core
Have you ever stopped to think about how big our home planet really is? The Earth's diameter in miles is more than just a number – it's a glimpse into the vastness of our world. From ancient civilizations to modern scientists, humanity has always been fascinated by the size of the Earth. It's like trying to measure the hugeness of a giant marble we all call home. So, buckle up because we're diving deep into the science, history, and fun facts behind the Earth's diameter in miles.
Understanding the Earth's diameter isn't just about numbers on a page. It's about appreciating the scale of our existence. Imagine trying to wrap your head around a planet that stretches over 7,900 miles from one end to the other. That's like driving from New York to Los Angeles and back again – and then some! This measurement isn't just random; it's the result of centuries of exploration and discovery.
But why does the Earth's diameter matter? Well, it plays a crucial role in everything from navigation to climate studies. Whether you're an aspiring astronaut or just someone who's curious about the world around you, knowing the Earth's diameter in miles gives you a better understanding of the planet we all share. So, let's explore this topic together and uncover the secrets of our world's size.
- Unveiling The Secrets Of April 15 Zodiac Aries Or Taurus Dive In
- Anuel Aa Siblings Unveiling The Family Dynamics Behind The Star
Why the Earth's Diameter in Miles Matters
Let's face it – the Earth's diameter in miles is more than just a cool fact to drop at parties. It's a fundamental measurement that affects everything from satellite orbits to global positioning systems. Think about it: how would we navigate without knowing the exact size of the planet? We'd be lost – literally!
Scientists use the Earth's diameter to calculate important things like gravity, atmospheric pressure, and even time zones. It's like having a blueprint for the planet. Without this knowledge, we wouldn't have accurate weather forecasts or the ability to send rockets into space. The Earth's diameter in miles is the foundation of modern science and technology.
How Scientists Measure the Earth's Diameter
Measuring the Earth's diameter isn't as simple as grabbing a ruler and calling it a day. Scientists use a combination of ancient techniques and modern technology to get the job done. One of the oldest methods is called "triangulation," where they measure angles and distances to calculate the Earth's size. It's like playing a cosmic game of connect-the-dots.
- Wheres The Party At Discover The Location Of Cma Awards
- Broward County Sheriff Inmate Search Your Ultimate Guide To Finding Inmate Records
Today, satellites and GPS systems provide even more precise measurements. By bouncing signals off the Earth's surface, scientists can determine the planet's diameter down to the inch. It's mind-blowing how far we've come from using sticks and shadows to relying on space-age technology. And guess what? The Earth's diameter in miles is still just as important as ever.
Earth's Diameter in Miles: The Numbers
So, what is the Earth's diameter in miles, anyway? Drumroll, please! The average diameter of Earth is approximately 7,917.5 miles. But here's the twist – the Earth isn't a perfect sphere. It's actually slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. This means the diameter varies depending on where you measure it.
At the equator, the diameter is about 7,926 miles, while at the poles, it's closer to 7,899 miles. Crazy, right? This difference might not seem like much, but it has a big impact on things like climate and ocean currents. The Earth's diameter in miles isn't just a single number – it's a range that tells us a lot about our planet's shape and structure.
Fun Facts About the Earth's Diameter
- The Earth's diameter is about 27 times smaller than the diameter of the Sun.
- If the Earth were the size of a basketball, its diameter in miles would be about the size of a pea.
- The Earth's diameter in miles is so vast that it would take a plane flying at 600 mph over 13 hours to travel across it!
These fun facts make the Earth's diameter in miles even more fascinating. It's like a cosmic puzzle waiting to be solved.
The History of Measuring the Earth's Diameter
Believe it or not, people have been trying to measure the Earth's diameter for thousands of years. One of the earliest attempts was made by a Greek mathematician named Eratosthenes around 240 BCE. Using nothing but a stick, some shadows, and a lot of brainpower, he calculated the Earth's diameter with surprising accuracy. His estimate was off by only about 100 miles – not bad for ancient technology!
Fast forward to the 17th century, and we see scientists like Sir Isaac Newton using gravity and math to refine these measurements. Today, we have tools like radar and laser ranging that give us pinpoint accuracy. But no matter how advanced our technology becomes, the Earth's diameter in miles remains a testament to human curiosity and ingenuity.
How Eratosthenes Did It
Eratosthenes' method was surprisingly simple. He noticed that on a certain day in the city of Syene (modern-day Aswan), the Sun was directly overhead and cast no shadow. At the same time, in Alexandria, a stick cast a shadow at an angle of about 7.2 degrees. Using this information, he calculated that the Earth's circumference was about 25,000 miles, which translates to a diameter of around 7,850 miles. Not too shabby for a guy with no satellites!
Modern Applications of the Earth's Diameter
Knowing the Earth's diameter in miles isn't just for scientists and geeks. It has real-world applications that affect our daily lives. For example, GPS systems rely on precise measurements of the Earth's size to determine location. Without this knowledge, your phone wouldn't be able to tell you where you are or how to get where you're going.
Airplane navigation, weather forecasting, and even satellite communication depend on accurate measurements of the Earth's diameter. It's like having a giant ruler that helps us understand and interact with the world around us. The Earth's diameter in miles might seem like a distant concept, but it's closer to home than you think.
Earth's Diameter and Climate Change
Did you know that the Earth's diameter in miles can help us understand climate change? By studying the planet's shape and size, scientists can model how heat is distributed across the globe. This information is crucial for predicting weather patterns and understanding the impact of rising temperatures. The Earth's diameter isn't just a number – it's a key to unlocking the mysteries of our changing climate.
Comparing Earth's Diameter to Other Planets
When it comes to size, Earth is pretty average in the grand scheme of things. But how does our planet's diameter stack up against its neighbors? Let's take a look:
- Mars: 4,212 miles
- Venus: 7,521 miles
- Jupiter: 86,881 miles
- Mercury: 3,032 miles
As you can see, the Earth's diameter in miles is right in the middle of the pack. We're not the biggest, but we're not the smallest either. This "Goldilocks" size is one of the reasons life can thrive on our planet. It's like being in the perfect spot for a cosmic sweet spot.
What Makes Earth's Diameter Unique?
While other planets might be bigger or smaller, Earth's diameter in miles is perfectly suited for life as we know it. The size of our planet affects everything from gravity to atmospheric composition. If the Earth were much larger or smaller, life as we know it might not exist. So, while the Earth's diameter in miles might not seem special at first glance, it's actually a key factor in making our planet unique.
Exploring the Earth's Layers
The Earth's diameter in miles isn't just about the surface – it's about what lies beneath. Our planet is made up of several layers, each with its own unique properties. From the crust to the core, every layer contributes to the Earth's overall size and structure.
The crust, where we live, is only about 20 miles thick on average. Beneath that lies the mantle, which stretches for thousands of miles. At the center of it all is the core, a dense ball of iron and nickel that's about 1,500 miles in diameter. These layers work together to create the Earth's diameter in miles we know today. It's like a giant cosmic onion, and we're just scratching the surface.
How the Earth's Layers Affect Its Diameter
The Earth's layers aren't just interesting – they're essential to understanding the planet's diameter. For example, the molten outer core creates the Earth's magnetic field, which protects us from harmful solar radiation. The solid inner core provides stability and helps regulate the planet's temperature. Without these layers, the Earth's diameter in miles would be very different – and life might not be possible.
Future Discoveries About the Earth's Diameter
While we know a lot about the Earth's diameter in miles, there's still so much to discover. Advances in technology are allowing scientists to study the planet's interior in ways we never thought possible. From seismic imaging to deep drilling projects, we're uncovering new insights into the Earth's size and structure every day.
Who knows what the future holds? Maybe we'll discover new layers or uncover secrets about the Earth's past that change our understanding of its diameter. The Earth's diameter in miles might seem like a solved mystery, but there's always more to learn. It's like peeling back the layers of a cosmic onion – each layer reveals something new and exciting.
What's Next for Earth Science?
Scientists are constantly working to refine our understanding of the Earth's diameter in miles. New technologies like gravitational wave detectors and deep-sea exploration vehicles are opening up new frontiers in Earth science. These discoveries could lead to breakthroughs in everything from climate science to space exploration. The Earth's diameter isn't just a number – it's a gateway to understanding the universe around us.
Conclusion: Why the Earth's Diameter Matters to You
So, there you have it – the Earth's diameter in miles isn't just a random factoid. It's a key to understanding our planet and its place in the universe. From ancient mathematicians to modern scientists, humanity has always been fascinated by the size of the Earth. And for good reason – it affects everything from navigation to climate science.
Now that you know more about the Earth's diameter in miles, why not share this knowledge with others? Leave a comment below or share this article with your friends. Who knows? You might inspire someone to become the next great Earth scientist. And remember, the Earth's diameter in miles is more than just a number – it's a reminder of the vastness and beauty of our world. Keep exploring, and never stop asking questions!
Table of Contents
- Why the Earth's Diameter in Miles Matters
- How Scientists Measure the Earth's Diameter
- Earth's Diameter in Miles: The Numbers
- Fun Facts About the Earth's Diameter
- The History of Measuring the Earth's Diameter
- How Eratosthenes Did It
- Modern Applications of the Earth's Diameter
- Earth's Diameter and Climate Change
- Comparing Earth's Diameter to Other Planets
- What Makes Earth's Diameter Unique?
- Exploring the Earth's Layers
- How the Earth's Layers Affect Its Diameter
- Future Discoveries About the Earth's Diameter
- What's Next for Earth Science?
- Gary In Remember The Titans The Unsung Hero You Need To Know
- Alaska Status The Ultimate Guide To Understanding Its Current State And Importance
The Earth whose diameter is 7,912 miles and is represented by the globe

Square Miles Surface Of The Earth The Earth Images
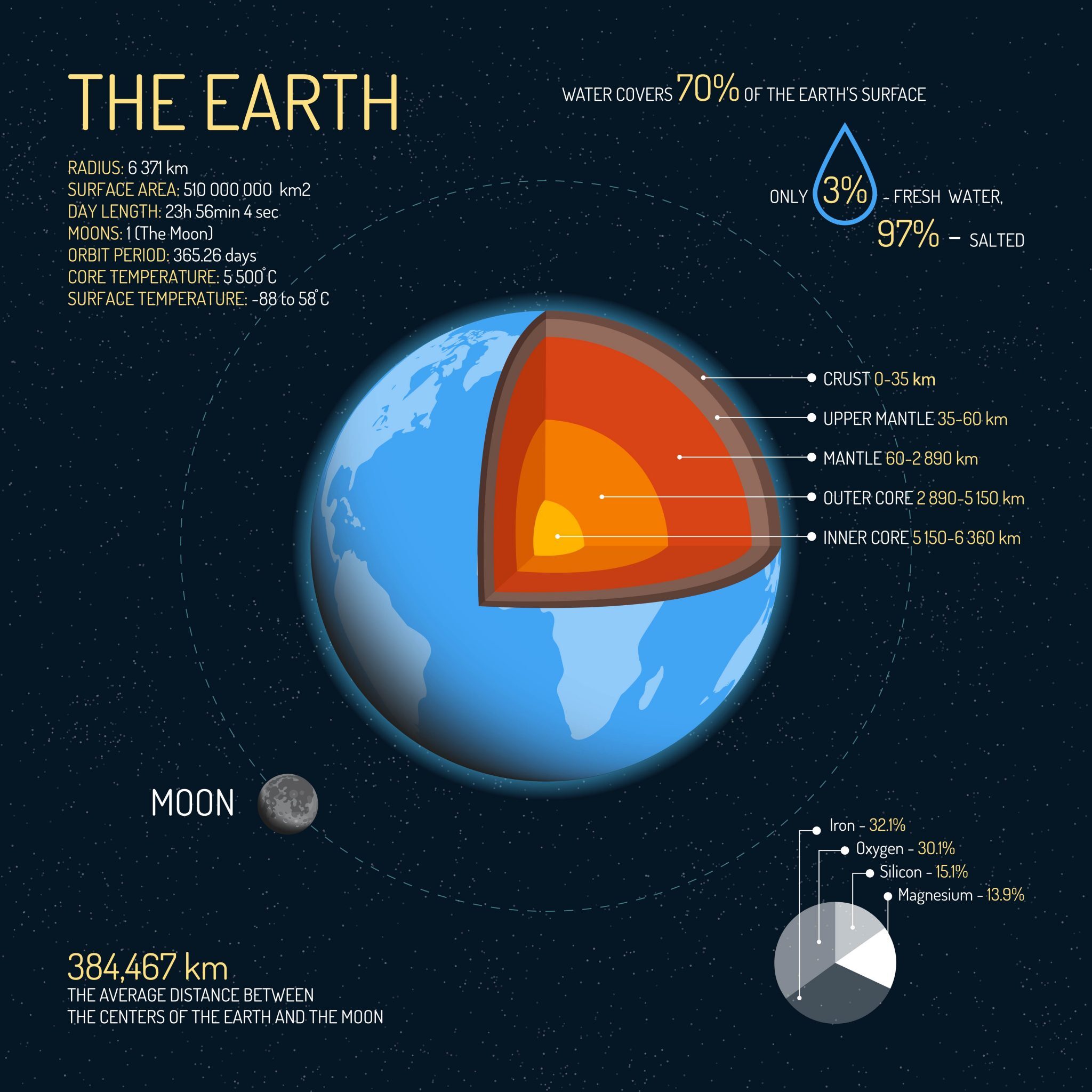
Earth Statistics StraightUp Stats of Earth Earth How